Euclid - Online edition
Eucalyptus stenostoma
Eucalyptus | Eucalyptus | Cineraceae | Stenostomae
Bark rough on lower trunk, compacted, shallowly fissured, grey; smooth bark yellow or creamy white; branchlets glaucous.
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stems round in cross-section, glaucous; juvenile leaves sessile until about node 3 then petiolate, becoming alternate by node 5–7, elliptical at first then ovate to lanceolate, to 18 cm long and 6 cm wide, slightly discolorous, green to grey-green or slightly glaucous.
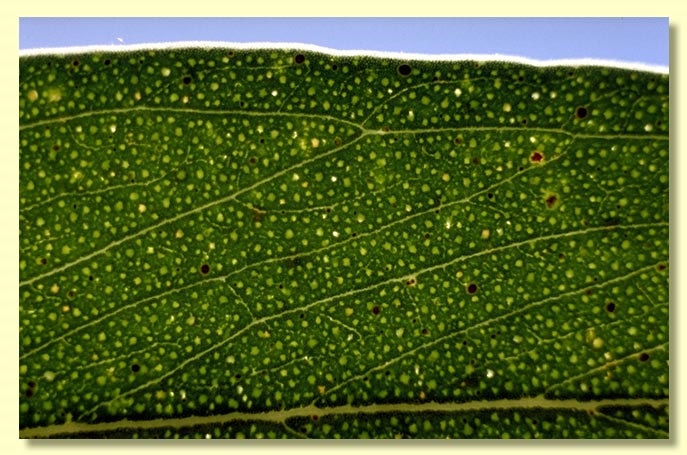
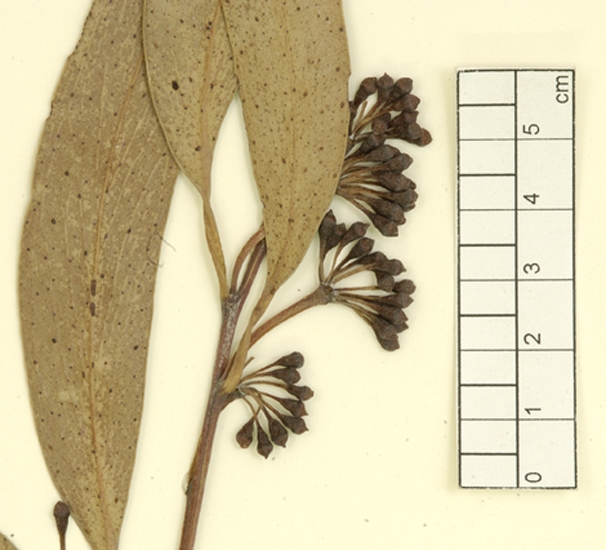
Adult leaves alternate, petiole 1–2 cm long; blade lanceolate to falcate, 9–19.5 cm long, 1–3 cm wide, base oblique or tapering to petiole, concolorous or slightly discolorous, glossy, green, side veins acute, sparsely reticulate or reticulation absent, intramarginal vein parallel to and well removed from margin, oil glands mostly island.
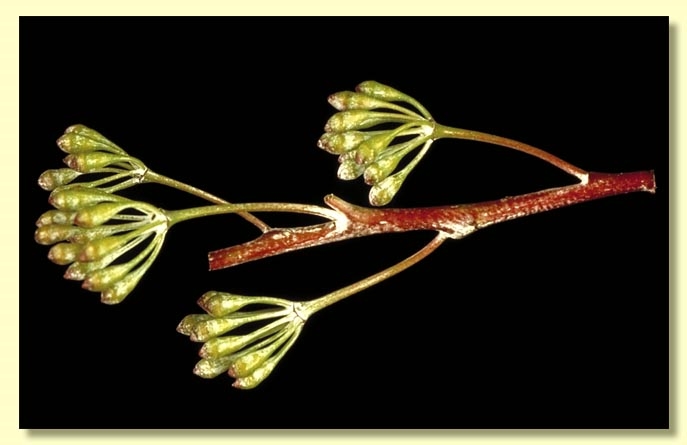
Inflorescence axillary unbranched, peduncle erect or recurved, 1.5–3 cm long, buds 13 to 19 or more per umbel, pedicels 0.4–1 cm long. Mature buds obovoid, 0.5–0.6 cm long, 0.3–0.4 cm wide, glaucous, scar absent, operculum conical to rounded, stamens inflexed, with outer staminodes, anthers reniform to cordate, versatile, dorsifixed, dehiscing by confluent slits, style short, stigma blunt or tapered, locules 3 or 4(5), the placentae each with 2 vertical ovule rows. Flowers white.
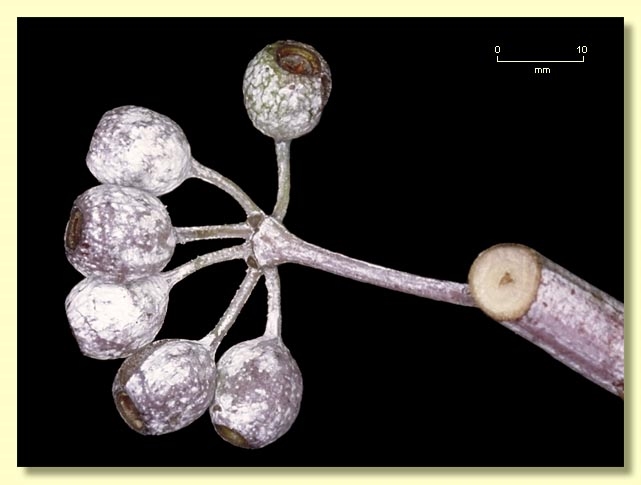
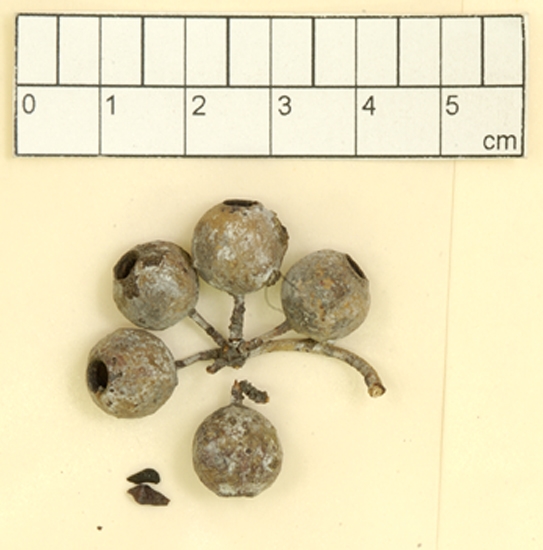
Fruit on pedicels 0.4–0.9 cm long, globular with a small orifice, 0.7–1.2 cm long, 0.6–1.2 cm wide, glaucous, disc descending, valves 3 or 4(5), enclosed.
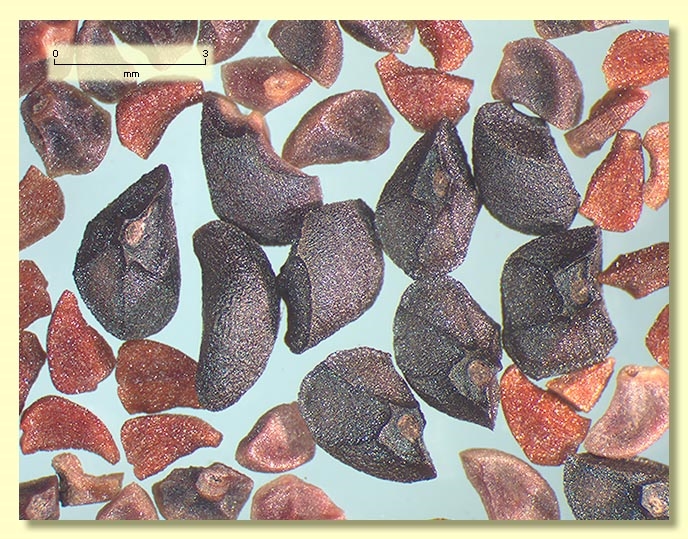
Seeds black, 1.5–3 mm long, pyramidal or obliquely pyramidal, dorsal surface usually smooth, hilum terminal.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons reniform; stems rounded in cross-section; leaves initially opposite and sessile to subsessile for 4–6 nodes then petiolate, alternate, ovate to elliptic, 5–10 cm long, 2.5–5 cm wide, base rounded to tapering, margin entire, apex pointed, glaucous or grey-green.
Flowering has been recorded in September and December.
A small to medium-sized tree scattered in the Tuross and Deua Rivers catchments of the eastern side of the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, often occurring in small pure stands on rocky hill tops.
E. stenostoma has a rough butt with white smooth bark above and may be confused with the more widespread E. fraxinoides, but differs in having more numerous buds in pendulous, glaucous clusters and globular fruit with a small orifice.
Eucalyptus stenostoma belongs in Eucalyptus subgenus Eucalyptus section Cineraceae having the following characters: cotyledons reniform, juvenile leaves alternate, bluish to glaucous, adult leaves with side-veins acute, single axillary inflorescences with buds in clusters of 13 up to 20, buds with single operculum, inflexed stamens, reniform anthers, ovules in two rows, and seeds more or less pyramidal. Within section Cineraceae, E. stenostoma is somewhat isolated by the combination of pendulous inflorescences, buds with some outer stamens lacking anthers (staminodes), style short, globular fruit and pronounced glaucescence of branchlets, buds, fruits and juvenile growth.