Euclid - Online edition
Eucalyptus morrisii
Eucalyptus | Symphyomyrtus | Exsertaria | Phaeoxylon
Eucalyptus morrisii R.T.Baker, Proc. Linn. Soc. New South Wales 25: 312 (1900).
T: New South Wales: Girilambone, W. Baeuerlen s.n., December 1899; Lectotype (NSW310761); fide Bean, A.R., Telopea 12(4): 473 (2010).
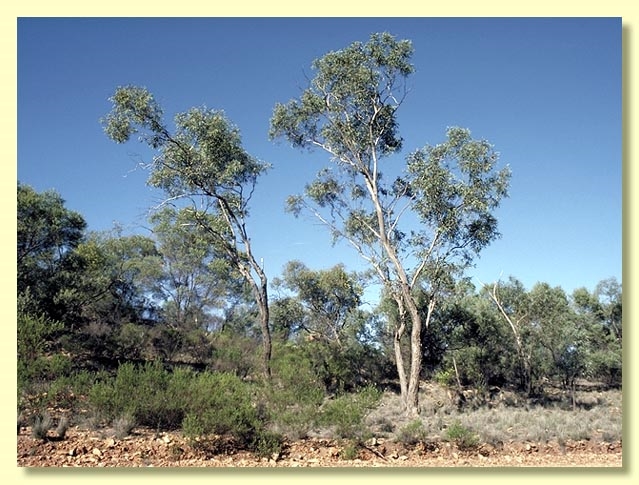
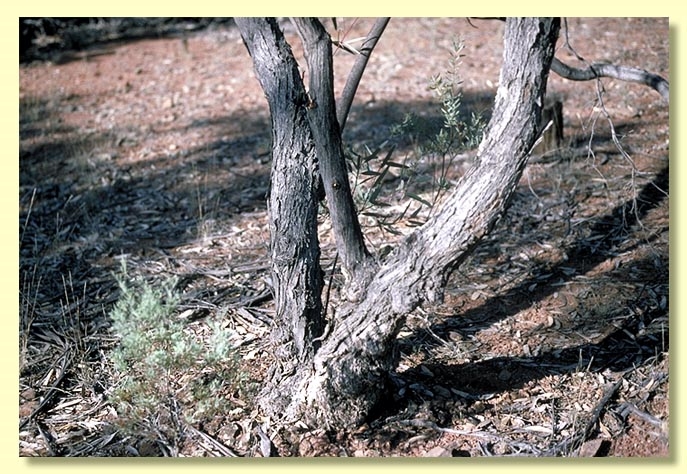
Bark of trees often rough to smaller branches, in mallees often only at base of stems; rough bark usually compacted, or fibrous or box-type, dark grey; smooth bark grey to green-grey, sometimes with a few ribbons in crown.
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stems usually square in cross-section; juvenile leaves shortly petiolate, opposite for 2–6 nodes then alternate, narrowly lanceolate to linear, 6–15 cm long, 0.5–2 cm wide, dull, green to grey-green.
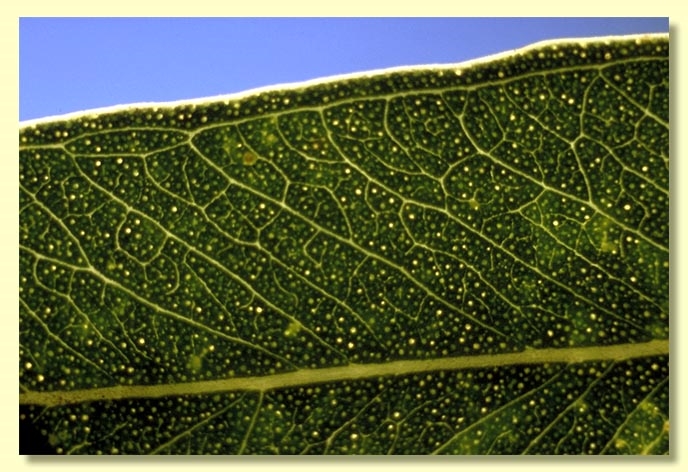
Adult leaves alternate, petiole 0.7–2 cm long; blade lanceolate, 5.5–14.5 cm long, 0.8–2.1 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, concolorous, dull, grey-green, side-veins greater than 45° to midrib, moderately reticulate, intramarginal vein parallel to and just within margin, oil glands island.
Inflorescence axillary unbranched, peduncles 0.5–1.3 cm long, buds 3 (rarely with a few in 7s), pedicellate (pedicels 0.2–0.3 cm long). Mature buds ovoid (0.8–0.9 cm long, 0.5 cm wide), yellow or creamy, scar present, operculum conical (0.5–0.7 cm long), stamens erect or irregularly flexed, anthers cuboid to oblong, versatile, dorsifixed, dehiscing by longitudinal slits (non-confluent), style long, stigma blunt, locules 4 to 6 each with 6 vertical ovule rows on the placenta. Flowers white.
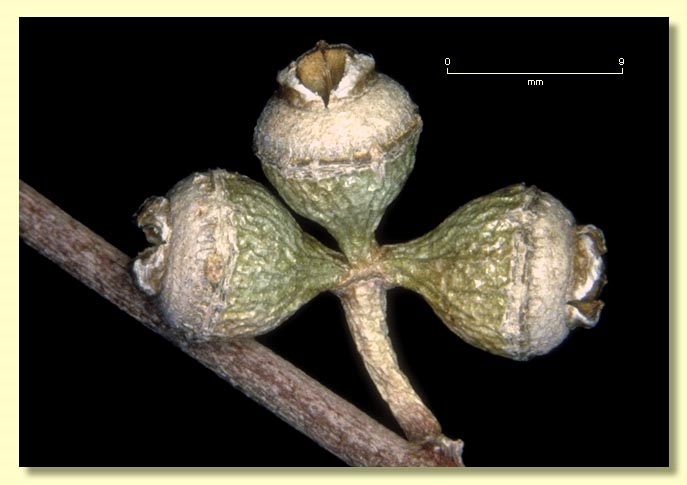
Fruit sessile or pedicellate (pedicels 0–0.3 cm long), hemispherical or obconical, 0.3–0.6 cm long, 0.7–1.2 cm wide, disc raised-convex or oblique, valves 4–6, strongly exserted.
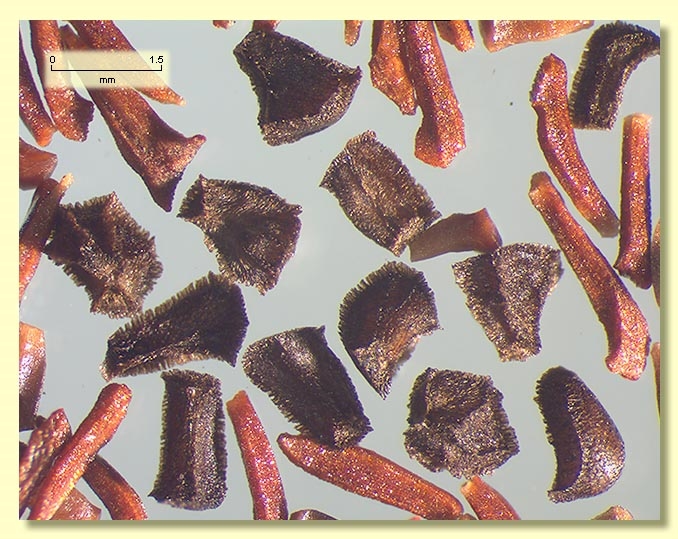
Seeds dark brown to black, 1–1.6 mm long, pyramidal or cuboid, dorsal surface usually pitted, hilum terminal.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons reniform to oblong; stems square to rounded in cross-section; leaves always petiolate, opposite for 3–6 nodes then becoming alternate, narrowly lanceolate to linear, 6–15 cm long, 0.4–2.3 cm wide, base tapering, apex pointed, dull, green to grey-green.
Flowering has been recorded in December.
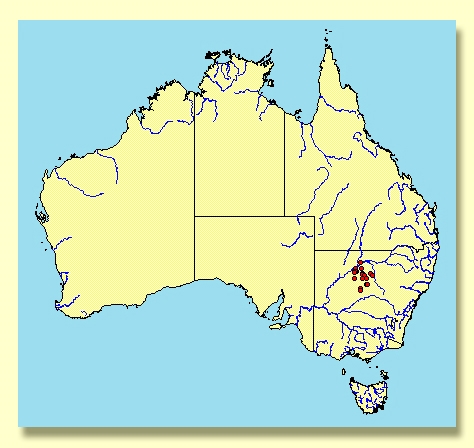
A mallee or rarely small tree scattered on rocky hills east of the Darling River in the Bourke–Cobar–Nyngan–Yathong area of north-western New South Wales. E. morrisii is distinguished by the extensive rough compacted or fibrous bark, linear juvenile leaves and three-budded inflorescences.
Eucalyptus morrisii belongs to a group of red gums that is distinguished by having rough bark, buds with the stamens mostly erect, fruit where the disc is united to the ovary roof and by the dark brown to black, toothed, cuboid to pyramidal single-coated seed. This group has six taxa occurring from central New South Wales north to New Guinea: E. brassiana, E. lockyeri subsp. lockyeri, E. lockyeri subsp. exuta, E. ammophila, E. exserta and E. morrisii. Within this group E. morrisii is the only species with three-budded inflorescences.
E. morrisii has been confused with E. flindersii, a 3 or 7- budded red gum endemic to South Australia, occurring mainly on slopes and summits of peaks in the Northern Flinders Ranges and also at Devil's Peak south-west of Quorn and Pualco Hill south of Yunta. E. flindersii is nearly always smooth-barked, with some of the larger plants having accumulated rough bark near the base. (E. morrisii is rough-barked on at least the trunk.)